Enterprise Payment Transformation: How Blockchain and Stablecoins Are Reshaping Global Finance
Cross-border B2B payments hit $150T+, but cost 3-5% & take days. Blockchain & stablecoins cut costs 80%, settle in minutes. Learn phased adoption paths, hybrid stablecoin tactics, & compliance-liquidity frameworks. See how Bosch, Walmart & Tesla cut fees & boost efficiency in global finance
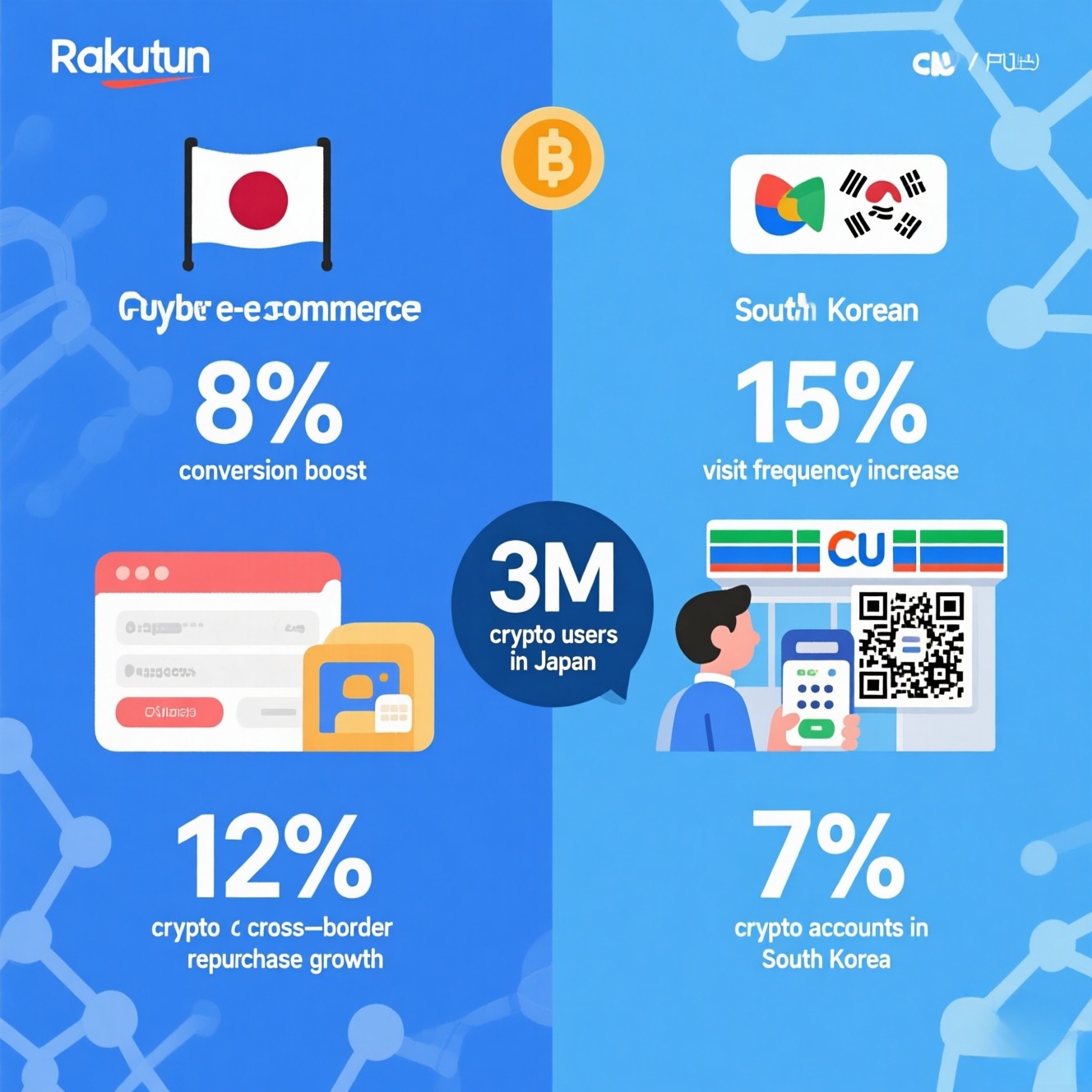
payment system innovation has become crucial for enterprises to improve efficiency and expand their boundaries. This is especially true for CFOs of multinational corporations, supply chain managers in manufacturing, or founders of e-commerce companies expanding into the Middle East and Latin America. The high costs, slow speeds, and low transparency of traditional cross-border payments are becoming increasingly prominent. How to securely, compliantly, and efficiently adopt digital currency payments is evolving from a technical issue to a strategic decision. This article, based on authoritative data and real-world cases, analyzes the gradual path, core strategies, and challenges of enterprises implementing blockchain and stablecoin payments, providing clear guidance for decision-makers.
I. Current Status and Pain Points: The Dilemma of Traditional Payments and the Dawn of Digital Currency
Payments Traditional cross-border payment systems have long been constrained by numerous intermediaries, lengthy settlement cycles, and high transaction fees. According to McKinsey's 2023 Global Payments Report, the cross-border B2B payment market has exceeded $150 trillion, but average transaction costs remain as high as 3-5%, and settlement cycles can take 2-5 business days. World Bank data further reveals that cross-border remittance costs in some emerging market countries exceed 10%. For companies engaged in manufacturing, trade, or supply chain management, such delays and high costs directly impact cash flow efficiency and exacerbate operational risks.
Against this backdrop, blockchain and stablecoin technologies offer the potential for structural changes in corporate payments. Enterprise blockchain payments can reduce cross-border transaction costs by up to 80%, achieve near-real-time settlement, and improve transaction transparency. According to a 2023 Deloitte survey, over 70% of financial institutions and large enterprises are evaluating or piloting blockchain-based payment solutions.
For example, German automotive parts giant Bosch piloted an Ethereum-based enterprise-grade blockchain payment gateway in its cross-border supply chain, successfully reducing payment times for some European-to-Asian suppliers from 72 hours to 20 minutes, saving over one million euros annually in fees. Another example comes from Singapore-based cross-border trade platform Linklogis, which, by integrating a blockchain payment system, has helped SMEs improve supply chain finance settlement efficiency by over 60%. These practices clearly reveal the real value of enterprises adopting digital currency payments: not only in efficiency improvements and cost savings, but also in achieving predictable, traceable, and programmable cash flows.
The TradeLens platform, developed by global shipping giant Maersk in collaboration with IBM, utilizes blockchain technology to digitize supply chain documents and automate payments, reducing customs clearance time from days to hours. Simultaneously, smart contracts automatically execute fee settlements, significantly reducing disputes and delays. In the retail sector, global luxury goods group LVMH, in partnership with Microsoft and ConsenSys, launched the AURA blockchain platform, integrating product traceability and cross-border B2B payments. This has improved the efficiency of payment settlements for its brands between Asia and Europe by over 50%.
II. Gradual Technology Integration: Implementation Path from Pilot to Deepening
For most traditional enterprises, a one-step, comprehensive adoption of digital currency payments is neither realistic nor secure. We recommend a "gradual technology integration path," proceeding steadily in stages and scenarios, specifically in the following three steps:
Phase 1: Internal Settlement Pilot
Enterprises can use customized stablecoins for small-scale trade settlements or subsidiary fund transfers within the group or with long-term trusted partners. The core objective of this phase is to test the stability, security, and compliance interface capabilities of the technology system. For example, a multinational technology company piloted the use of a USD-pegged stablecoin for internal account settlements between its Asia-Pacific branches, reducing exchange rate conversion costs and initially building internal finance personnel's understanding and operational capabilities regarding digital currency payments.
Phase 2: Supply Chain Scenario Expansion
After the pilot verification proves feasible, enterprises can extend the payment solution to core suppliers or distribution networks. Utilizing smart contracts to implement conditional payments (such as "cash on delivery" or "automatic settlement after acceptance") can significantly optimize cash flow management and enhance supply chain collaboration efficiency. For example, a Chinese home appliance manufacturer connected its blockchain payment system to its upstream component suppliers, using smart contracts to stipulate automatic payment triggering within 24 hours of delivery, which both increased suppliers' willingness to cooperate and reduced the company's own financial reconciliation workload. US retail giant Walmart deployed a blockchain payment system based on Hyperledger Fabric in its Canadian fresh food supply chain, enabling automated reconciliation and payments from farm to warehouse, reducing the settlement cycle from an average of 30 days to 48 hours, while ensuring the authenticity of food traceability data. Another typical example is Tesla, which accepts Bitcoin payments for some of its raw material purchases and, after a pilot program, included stablecoins (such as USDC) in its global supplier payment options to mitigate the risks of cryptocurrency price volatility.
Phase 3: Ecosystem Integration and Global Expansion
In this phase, companies can further connect to third-party enterprise-grade blockchain payment gateways, linking fiat currencies with various digital currencies to achieve global payment collection, automatic currency exchange, and real-time fund management. For example, by partnering with payment service providers such as Circle and Strip, companies can process stablecoin or fiat currency payments from different countries within a single system, with the system automatically handling compliance checks, currency conversions, and accounting records.
The key to success in this path lies in selecting suitable payment tools. We propose a "hybrid stablecoin customization strategy," which combines fiat-backed stablecoins (such as USDC and USDP) with compliant asset-backed tokens, tailoring a hybrid solution based on the company's business region. For example, operating in the Middle East requires compliance with the regulatory requirements of the UAE's ADGM or Saudi Arabia's SAMA, and stablecoins recognized by local regulators can be used. In Southeast Asia, partnering with local digital banks to issue regional stablecoins can be considered to better balance payment stability, compliance, and operational flexibility.
Cross-border payment company Ripple has partnered with Japan's SBI Holdings to provide XRP-based instant settlement services for trade between SMEs in Japan and South Korea, reducing cross-border remittances from 2-3 days to within 2 minutes, and lowering fees by approximately 70%. In Latin America, Brazilian fintech company EBANX has partnered with Visa to launch a stablecoin payment channel, helping global e-commerce companies receive Brazilian Real payments and convert them to USDC in real time, effectively addressing the challenges of high inflation and exchange rate volatility in the region.
III. Compliance and Liquidity: Building a Dual Guarantee for Enterprise-Level Payments
The two core challenges enterprises face in promoting blockchain payments are compliance alignment and liquidity management. These two aspects must be systematically planned and constructed simultaneously.
Constructing a Compliance Mapping Framework
Different jurisdictions have significantly different regulatory policies regarding digital currencies. Enterprises need to build a "compliance mapping framework" that systematically embeds the licensing requirements, anti-money laundering rules, customer identity verification processes, and tax filing nodes of the countries involved in their business (such as Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Europe) into the payment process. For example, using a gateway solution compliant with the Travel Rule can achieve full auditability and regulatory oversight of transactions. The virtual asset service provider licensing system launched in Hong Kong in 2023 and the MiCA regulation introduced by the European Union provide clear compliance guidance for enterprises, while also requiring enterprise payment systems to have a high degree of regulatory adaptability.
Liquidity Depth and Risk Management
When enterprises adopt stablecoin payments on a large scale, they need to avoid slippage losses or exchange delays caused by insufficient market depth. To address this, companies should establish a "liquidity depth game model," dynamically allocating funds across multiple liquidity pools (such as decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Curve, and compliant centralized exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken), and designing hedging strategies in cooperation with market makers to ensure controllable costs during large-scale redemptions. Furthermore, corporate finance departments need to establish a credit risk assessment mechanism for stablecoin issuers, prioritizing stablecoins with transparent reserve assets and regularly published audits.
Example of a scenario-based application
A founder of a cross-border e-commerce company operating in the Middle East faced the challenge of high inflation and currency volatility. By integrating a blockchain payment path that supports automatic conversion between USDC and local currencies, their e-commerce platform not only provides buyers with stablecoin payment options but also uses smart contracts to convert sales revenue into USD assets in real time, effectively mitigating the risk of local currency devaluation. Simultaneously, leveraging the traceability of blockchain, the platform achieves clear recording of the source of each transaction, easily passing local anti-money laundering audits and gaining the trust of regulatory agencies and partners.
In 2023, global cross-border payment platform PayPal launched its stablecoin PYUSD and integrated it into its B2B payment network, providing SMEs with end-to-end services from invoice generation to blockchain settlement. Businesses can directly pay overseas suppliers with PYUSD through the PayPal platform, automatically generating transaction records compliant with the tax requirements of multiple countries. Another example comes from African fintech company Flutterwave, which partnered with Stellar Blockchain to provide stablecoin-based cross-border payment services for businesses in Nigeria, Kenya, and other regions. This helps local exporters quickly convert USD payments into local currency, avoiding the week-long clearing delays and up to 8% fees associated with traditional banking channels.
IV. Cognitive Reshaping and Industry Opportunities: From Education to Value Realization
Building a technological system is only the foundation; successful implementation ultimately depends on "reshaping user cognitive anchors"—that is, transforming digital currency payments from an "unfamiliar technical concept" into a "superior payment option" through user-friendly interface design, continuous user education, and effective incentive mechanisms. Especially in the token payment scenario of the gaming industry, by linking in-game points to stablecoins, players can exchange assets in real time, significantly increasing user stickiness and ecosystem value. For example, gaming platforms like Axie Infinity, by building an endogenous blockchain-based economy, have not only achieved seamless payments between global players but also created a completely new model for digital asset circulation.
This provides important insights for traditional enterprises transforming into digital currency payment systems: payment innovation is not merely a technological upgrade but also a reshaping of user experience and business models. Manufacturing companies can expand supply chain finance through tokenized accounts receivable; trading companies can utilize smart contracts for automated revenue sharing and real-time settlement; and e-commerce platforms can leverage stablecoins to lower the barriers to cross-border payments and attract global consumers. The evolution of the payment process is gradually becoming a new frontier in enterprise digital competition.
Starbucks, the global coffee chain, is testing a blockchain points system in its "Starbucks Rewards" program. Members can accumulate and use tokenized rewards through digital wallets, which can then circulate among partner merchants, enhancing user loyalty and ecosystem synergy. In the manufacturing sector, Siemens Energy tokenizes its green energy certificates and uses a blockchain platform for peer-to-peer trading and settlement with suppliers and customers, achieving real-time pricing and automated payment for carbon credit assets.
Conclusion: A Reliable Roadmap to the Future of Payments
The digital transformation of enterprise payment systems is no longer a question of "whether to do it," but rather "how to do it well." From gradual integration paths and customized stablecoin strategies to the construction of compliance and liquidity frameworks, each step requires professional planning and the support of reliable technology partners. In the next three to five years, with the launch of central bank digital currencies and the gradual unification of cross-border payment standards, the enterprise payment ecosystem will further evolve towards efficiency, transparency, and programmability.
We understand the CFO's requirement for financial controllability, the supply chain manager's pursuit of efficiency, and the keen market insight of pioneers going global—the success of digital currency payment solutions begins with a clear path and is achieved through professional collaboration. In this era of rapid change, early planning and steady progress will help enterprises gain an efficiency advantage and innovative initiative in the new era of payments.
For customized payment transformation assessments tailored to your industry (manufacturing, trade, e-commerce, or gaming), please contact us to obtain a personalized roadmap report. Let's explore the certainty of the future of payments together.
.svg)
Payments designed to accelerate your business
Choose Nuvei for payments that work harder to convert sales and boost your bottom line.




